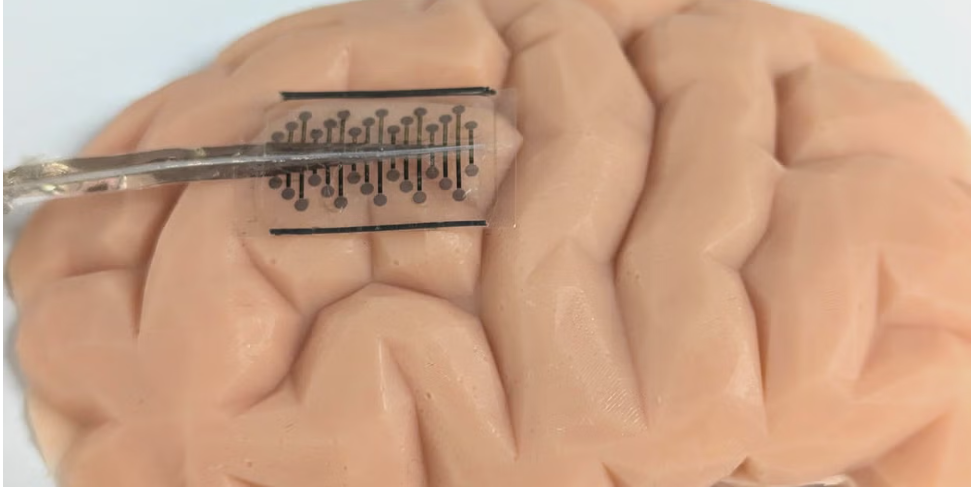
A research team led by the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge have created new ‘origami-inspired’ brain electrodes that can fold up to a fraction of their full size. This advance could significantly reduce the amount of surgery needed to treat conditions such as epilepsy, or to install brain-computer interfaces.